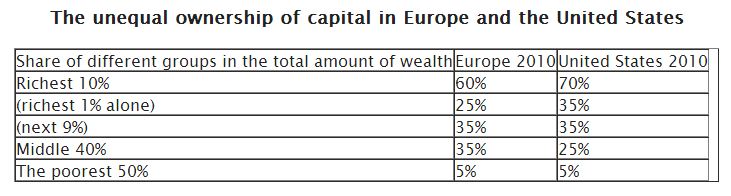
Thomas Piketty has just published a massive new book tackling the explosive growth in income inequality. Here’s what it looked like in Europe and the United States in 2010:
A New York Times review of the book, Capital in the Twenty-First Century, begins as follows:
What if inequality were to continue growing years or decades into the future? Say the richest 1 percent of the population amassed a quarter of the nation’s income, up from about a fifth today. What about half?
To believe Thomas Piketty of the Paris School of Economics, this future is not just possible. It is likely….
His most startling news is that the belief that inequality will eventually stabilize and subside on its own, a long-held tenet of free market capitalism, is wrong. Rather, the economic forces concentrating more and more wealth into the hands of the fortunate few are almost sure to prevail for a very long time.
Piketty’s pessimistic view is based on his argument that income generated from capital normally grows faster than the economy or income from wages. This means that the private owners of capital benefit disproportionately from growth, which makes it easier for them to increase their asset holdings and by extension future income. And, since wealth and income translate into political power, we face a self-reinforcing dynamic leading to ever growing inequality.
This suggests that embracing a system based on maximizing the returns to private owners of capital is a mistake for the great majority of working people. A recent study by the investment bank Credit Suisse provides more evidence for this conclusion. As Michael Burke explains:
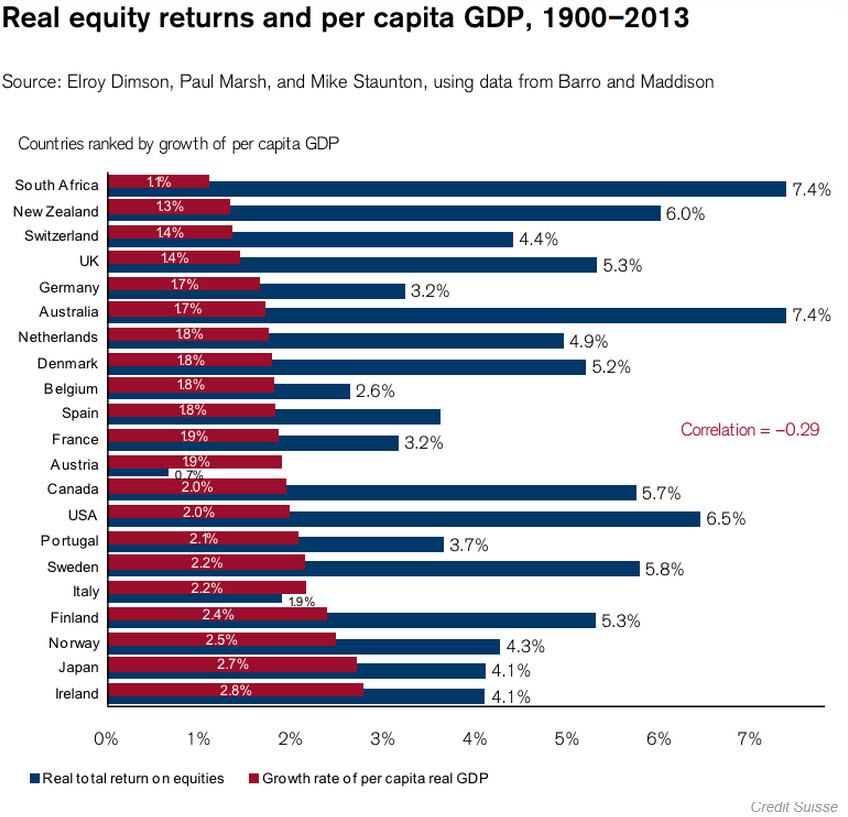
The study … shows that long-term growth rates of GDP in selected industrialized economies are negatively correlated with financial returns to shareholders.
That is, the best returns for shareholders are from countries where GDP growth has been slowest, and vice versa. Where growth has been strongest, shareholder returns are weakest….
The negative correlation [seen in the chart below] does not prove negative causality. But it does support the theory which suggests that the interests of shareholders are contrary to the interests of economic growth and the well-being of the population.
All of this information is worth keeping in mind the next time business and political leaders tell us that the key to our well-being is boosting business confidence, the market, or private returns on investment.
This post originally appeared on Sociological Images, a Pacific Standard partner site, as “Why Income Inequality Will Likely Keep Getting Worse.”





